Artistudio Technical
WordPress.md
Wordpress Quick Start Guide - A Modern Way to Develop & Conquer a Website

WordPress is a free and open-source content management system (CMS) that is widely used to create websites and blogs. It was first released in 2003, and has since become one of the most popular CMS platforms in the world, powering over 40% of all websites on the internet.
WordPress is built using PHP and MySQL, and features a user-friendly interface and a powerful plugin architecture that allows developers to add functionality to the platform. It also includes a large community of users and developers who contribute to the platform through themes, plugins, and support resources.
Overall, WordPress is a flexible and customizable platform that can be used to create a wide range of websites and online applications. Its popularity and large community of users make it a reliable choice for building websites of all sizes and complexities.
What is WordPress used for?
WordPress is used by a wide range of individuals and organizations, including bloggers, small businesses, non-profits, and large corporations. It is particularly well-suited for creating websites with dynamic content, such as :
- Blogging: WordPress was originally developed as a blogging platform, and it remains a popular choice for bloggers of all kinds. It provides powerful tools for creating, organizing, and publishing blog posts, as well as managing comments and user engagement.
- Business Websites: Many businesses use WordPress to build their websites because of its ease of use and flexibility. It allows businesses to showcase their products and services, provide contact information, and even set up online stores with e-commerce plugins.
- E-commerce: With the help of plugins like WooCommerce, WordPress can be transformed into a full-fledged e-commerce platform. This allows businesses to sell products and services online, manage inventory, process payments, and handle shipping and delivery.
- Portfolio and Personal Websites: Artists, photographers, designers, and other creative professionals often use WordPress to showcase their work in an attractive and professional manner. Customizable themes and portfolio plugins make it easy to create visually appealing portfolios.
- Non-profit and Educational Websites: WordPress is widely used by non-profit organizations and educational institutions to create websites that promote their causes, share information, and engage with their communities.
- Community and Membership Websites: WordPress can be used to create community forums, social networking sites, and membership websites where users can interact with each other, share content, and access exclusive content.
- Online Magazines and News Websites: Many online magazines and news outlets use WordPress to publish and organize their articles, making it easy for readers to navigate and discover content.
- Event Websites: WordPress can be used to create event websites for conferences, workshops, festivals, and other gatherings. Event management plugins can help with ticketing, scheduling, and registration.
- Personal Blogs and Journals: Individuals use WordPress to create personal blogs and online journals, where they can share their thoughts, experiences, and insights with the world.
- Government Websites: Some government agencies and departments use WordPress to manage and share information with the public, such as announcements, policies, and services.
Why should I use WordPress?
There are several compelling reasons to consider using WordPress for building your website:
- Ease of Use: WordPress is known for its user-friendly interface and intuitive content management system. Even users with limited technical knowledge can quickly learn to create and manage their website without much difficulty.
- Extensive Themes and Plugins: WordPress offers a vast library of themes and plugins that allow you to customize the look and functionality of your website. Whether you need a simple blog or a complex e-commerce platform, there's a wide range of options available to suit your needs.
- Flexibility and Customization: WordPress is highly flexible and can be used to create any type of website, from personal blogs to business websites, online stores, portfolios, and more. You have complete control over the design and layout of your site, allowing you to create a unique online presence.
- SEO-Friendly: WordPress is designed with SEO in mind, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site. Additionally, there are various SEO plugins available to help optimize your content and improve your search engine rankings.
- Mobile Responsiveness: Many WordPress themes are mobile-responsive, meaning your website will automatically adjust and look great on various devices, including smartphones and tablets.
- Active Community and Support: WordPress has a large and active community of developers, designers, and users who contribute to its continuous improvement. This means you can find answers to your questions and access support resources easily.
- Regular Updates and Security: The WordPress team regularly releases updates and security patches to keep the platform safe and secure. Staying up-to-date ensures your website is protected from potential vulnerabilities.
- Scalability: Whether you have a small personal blog or a large enterprise website, WordPress can scale to meet your needs. It can handle high traffic and large amounts of content without compromising performance.
- Cost-Effective: WordPress is an open-source platform, which means it is free to use. While you may need to invest in themes or premium plugins for specific features, the overall cost of building and maintaining a WordPress website is typically lower compared to other platforms.
- Integration with Third-Party Tools: WordPress integrates seamlessly with various third-party tools and services, such as email marketing platforms, social media, analytics, and more, enhancing the functionality and efficiency of your website.
Getting Started, How do I use WordPress?
You can follow any of these tutorial :
- [Overview of WordPress (Beginners Guide 2020)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jmqu4HC3zmo "Play video "Overview of WordPress (Beginners Guide 2020)"")
- How To Make a Website With WordPress (Beginners Tutorial)
- WordPress Tutorial - How to Make a WordPress Website for Beginners
Pro and Cons
Using WordPress has its advantages and disadvantages, as with any other website platform. Here are some of the pros and cons of using WordPress:
Pros:
- Ease of Use: WordPress is known for its user-friendly interface and intuitive content management system, making it easy for beginners to create and manage their websites.
- Customization: With a vast library of themes and plugins, WordPress allows you to customize the look and functionality of your site to fit your specific needs and preferences.
- Flexibility: WordPress can be used to build a wide variety of websites, from simple blogs to complex e-commerce stores and corporate websites.
- SEO-Friendly: WordPress is designed with search engine optimization (SEO) in mind, making it easier for your website to rank higher in search engine results.
- Active Community: WordPress has a large and active community of developers, designers, and users who contribute to its continuous improvement and offer support.
- Regular Updates: WordPress regularly releases updates and security patches, ensuring that your website stays secure and up-to-date.
- Mobile Responsiveness: Many WordPress themes are mobile-responsive, ensuring that your website looks good and functions well on different devices.
Cons:
- Security: Being a popular platform, WordPress can be a target for hackers. It is crucial to keep your themes, plugins, and core WordPress installation up-to-date to minimize security risks.
- Performance: With a large number of plugins and customizations, WordPress websites can sometimes experience performance issues. Proper optimization is necessary to maintain fast loading times.
- Learning Curve: While WordPress is user-friendly, there may still be a learning curve for beginners, especially when dealing with more complex customizations.
- Compatibility Issues: Some themes and plugins may not be fully compatible with each other, leading to potential conflicts that could affect your website's functionality.
- Dependency on Plugins: While plugins provide added functionality, relying too heavily on them can increase the risk of compatibility issues and potential security vulnerabilities.
- Need for Regular Maintenance: WordPress websites require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and security. This includes updating themes, plugins, and backups.
- Limited Control for Complex Needs: While WordPress is flexible, for very complex websites with unique requirements, a fully custom solution may be more suitable.
File Structure
In a typical WordPress installation, the file structure consists of various files and directories, each serving a specific purpose. Here's a list of key files and directories in WordPress and their primary usage:
wp-admin/: This directory contains files and subdirectories related to the WordPress administration dashboard.wp-content/: This directory contains files and directories related to the content of your website, such as themes, plugins, uploads, and other media files.plugins/: This directory is where you can install and manage WordPress plugins. Each plugin typically resides in its own subdirectory within theplugins/directory.themes/: This directory is where you can install and manage WordPress themes. Each themes typically resides in its own subdirectory within thethemes/directory.uploads/: This directory is used to store media files uploaded through the WordPress media library, such as images, videos, and documents.
wp-includes/: This directory contains core WordPress files and libraries, including functions, classes, and script files.wp-config.php: This file is the main configuration file for your WordPress installation. It contains database connection details, security keys, and other important settings..htaccess: This file is used for configuring Apache server settings and is often used to enable features like URL rewriting or improve website security.index.php: This is the main entry point for your WordPress site. It loads the WordPress environment and starts the page rendering process.
Database
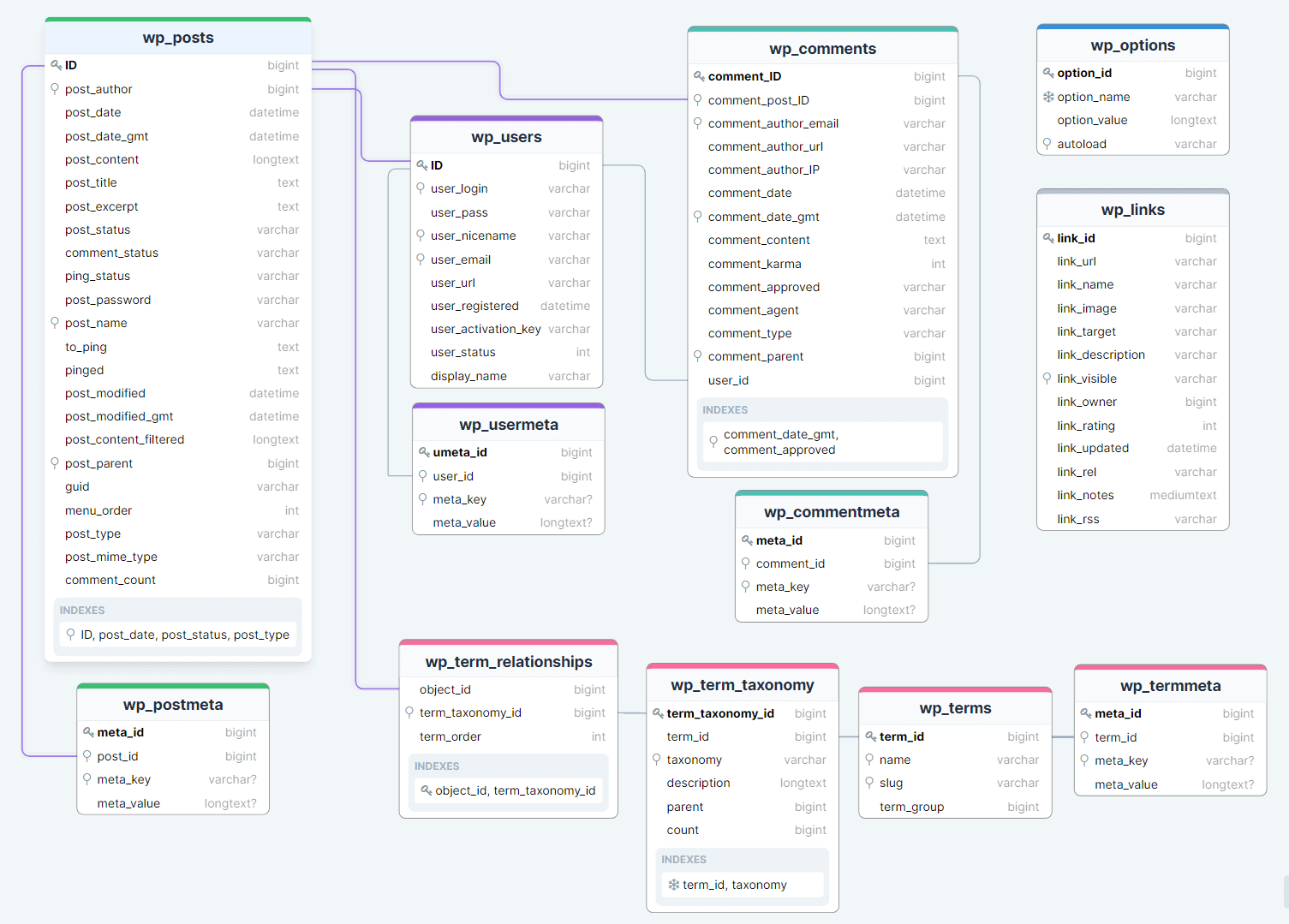 Here are some of the common WordPress database tables and their purposes:
Here are some of the common WordPress database tables and their purposes:
wp_posts: Stores all the posts, pages, and custom post types in your WordPress site.wp_users: Contains user information such as usernames, passwords, email addresses, and user roles.wp_comments: Stores comments made on your posts and pages.wp_terms: Manages taxonomy terms, such as categories and tags.wp_term_taxonomy: Defines the taxonomies and their relationships to terms in the wp_terms table.wp_term_relationships: Establishes the relationships between posts and their taxonomy terms.wp_options: Stores various WordPress settings and configurations.wp_postmeta: Stores additional metadata for posts, such as custom fields and post revisions.wp_usermeta: Stores additional metadata for users, such as user-specific settings and custom fields.wp_links: Manages blogroll links (deprecated in newer versions of WordPress).wp_woocommerce_*: A set of tables specific to WooCommerce, the popular eCommerce plugin for WordPress, which stores information related to products, orders, customers, and more.wp_*_log: Various tables with prefixes like wp_debug_log, wp_error_log, wp_cron_log, which store different types of logs for debugging and troubleshooting purposes.
WordPress Architecture
- WordPress Core Codebase:
- The WordPress core consists of the main PHP code that powers the website. This includes the core files responsible for functions such as user management, the admin dashboard, posts, pages, themes, plugins, media management, and the database connection.
- WordPress is built using PHP, MySQL, and JavaScript, with CSS and HTML for styling and structure.
- Contributing to the WordPress Core:
- WordPress is an open-source project, meaning that anyone can contribute to its development. Developers can contribute code to the WordPress core by reporting bugs, suggesting new features, writing patches, or directly contributing code through the WordPress Trac system or GitHub.
- Contributors: Many developers from the WordPress community contribute to the core development, including volunteers, contributors from WordPress-related businesses, and individual developers.
- Core Contributors: These are the dedicated developers who contribute frequently to the development of the WordPress core. They help in making decisions regarding the software, reviewing patches, and ensuring the overall integrity of the platform.
- WordPress Core Features:
- Themes & Templates: WordPress core includes basic theme functionality to allow the design and layout of a website. Developers can extend it through custom themes.
- Plugins API: WordPress core provides a framework for plugins to extend and enhance its functionality. Developers can create plugins that interact with the core system.
- Custom Post Types & Taxonomies: These features allow users and developers to create custom content types and categorization systems for a website, beyond the standard posts and pages.
- Widgets & Menus: WordPress allows developers to create custom widgets and menus that can be added to the site's theme to enhance its functionality.
- Admin Interface: The admin dashboard is a key feature of WordPress that allows site owners and administrators to manage the content, settings, and plugins of the site. Core development involves creating and improving this interface.
- APIs and Libraries:
- WordPress core provides various APIs to interact with and extend its functionality. These include:
- REST API: Allows developers to access and interact with WordPress content and settings via external applications.
- Database API: Handles database interactions and queries for retrieving or storing data.
- User API: Manages user authentication, profiles, roles, and permissions.
- Theme & Plugin APIs: These allow developers to build themes and plugins that can extend or modify WordPress functionality.
- WordPress core provides various APIs to interact with and extend its functionality. These include:
- Version Releases and Updates:
- WordPress follows a regular release cycle that includes major, minor, and maintenance releases. New features are typically introduced in major releases, while minor releases include bug fixes, security patches, and small improvements.
- Developers involved in core development are responsible for planning, testing, and maintaining these releases to ensure they meet high-quality standards.
- Backwards Compatibility:
- One of the key principles of WordPress core development is maintaining backwards compatibility. This ensures that websites built with older versions of WordPress continue to work as expected when the core is updated. However, while backwards compatibility is important, core development also strives to improve functionality, introduce new features, and fix security vulnerabilities.
- Testing:
- Testing is a crucial part of WordPress core development. Developers write unit tests and perform integration testing to ensure that new code doesn't break existing functionality.
- Automated testing tools are also used to streamline the process, ensuring that every change is thoroughly tested for bugs and regressions.
WordPress Core Development Workflow:
- Trac & GitHub: WordPress development uses Trac, a bug-tracking and project management system, and GitHub repositories to track issues, submit patches, and manage code contributions.
- Contributor Workflow: Developers submit patches or pull requests (PRs) to contribute to the WordPress core. These are reviewed by experienced contributors, who approve, reject, or request changes to the code.
- Release Management: Once new features or bug fixes are ready, they are packaged into new releases of WordPress. These updates are then tested and pushed out to millions of websites via the automatic update system.
How to Get Involved in WordPress Core Development:
- Join the Community: Anyone can get involved in WordPress core development by joining the WordPress contributor community. There are multiple ways to contribute, such as fixing bugs, reporting issues, writing documentation, or helping with translations.
- Testing and Feedback: Developers and users can participate in beta testing of new features before they are released to the public. Providing feedback on new features helps ensure the quality of the platform.
- Contribute Code: If you’re a developer, you can start by contributing to the codebase. WordPress has a well-documented coding standard and contribution process, so developers can begin by fixing minor bugs or improving existing features.

- Official Website - Make WordPress
- Meetup Organizer
- WordCamp Organizer
- Community Deputy
- WordCamp Mentor
- Team Rep
- Meetup Reactivation Supporter
- Polyglots
- Pledges
- Five for the Future
- Rosetta for the Community :
Lists of Indonesian WordPress Plugins & Themes
Tutorials
- Installation
- Configuration
- Hosting
- Plugins
Resources
Official
-
Official Plugins
-
StackExchange
-
News & Blog
-
YouTube Channel
- LivingWithPixels
- WP Beginners
- WP Casts Wikipedia Indonesia
-
: 2025-03-23